- 백기선 님이 유튭에서 진행하는 JAVA Live-study 과정을 기록한다.
- 매 주 이슈에 올라온 질문들에 대해 공부하고 답을 남기고, 이슈에 링크를 공유하는 방식으로 진행된다. 추후 백기선 님의 유튜브 라이브를 통해 피드백을 받게 된다.
즉, Java 공부를 기록하는 과정이다 🌱
📌 목표
자바가 제공하는 제어문을 학습하세요.
📌 학습할 것 (필수)
- 선택문
- 반복문
제어문이란?
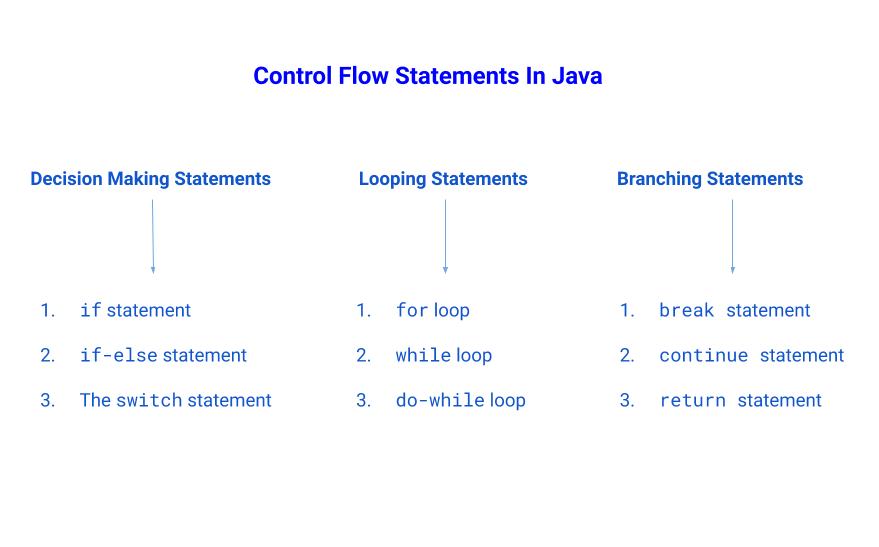
제어문(Control-flow statement)은 프로그램의 실행 순서를 제어할 수 있게 한다. Java의 제어문은 decision making, branching, looping, conditional block이 있다.
(이미지 출처: https://soshace.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/untitled-drawing.jpg)
Decision making statements(선택문)
if statement
if 문은 expression과 statement로 이루어져 있다. expression이 참이 되는 경우, 인터프리터가 statement를 실행하고, expression이 거짓이 되는 경우, 그 statement를 스킵한다.if (username == null) // If username is null, username = "John Doe"; // use a default value(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
if-else statement
if 문은 또한 선택적으로 else 키워드를 함께 사용할 수 있다. expression이 참이라면 첫 번째 statement를 실행하고, 거짓이라면 두 번째 statement를 실행하게 된다.if (username != null) System.out.println("Hello " + username); else { username = askQuestion("What is your name?"); System.out.println("Hello " + username + ". Welcome!"); }(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
else-if clause
만약, 여러 블록의 코드 중 선택해야한다면 else-if 절을 사용한다.if (n == 1) { // Execute code block #1 } else if (n == 2) { // Execute code block #2 } else if (n == 3) { // Execute code block #3 } else { // If all else fails, execute code block #4 }(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
switch statement
만약, 하나의 변수 값에 따라 선택지가 결정된다면, 여러 개의 if 구문을 대신하여 switch 문을 사용할 수 있다.switch(n) { case 1: // Start here if n == 1 // Execute code block #1 break; // Stop here case 2: // Start here if n == 2 // Execute code block #2 break; // Stop here case 3: // Start here if n == 3 // Execute code block #3 break; // Stop here default: // If all else fails... // Execute code block #4 break; // Stop here }(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
Looping statements(반복문)
while statement
while 문은 Java의 기본적인 반복문이다.
expression의 참/거짓을 판별하여(boolean 또는 Boolean이 결과값인 작업) 거짓이라면 반복문을 종료하고 다음 구문으로 이동한다. 참이라면 반복이 재개되며 expression의 참/거짓이 다시 평가된다.int count = 0; while (count < 10) { System.out.println(count); // 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 count++; }(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
do statement
do 또는 do-while 문은 while 문과 비슷하다. while 문은 참/거짓을 판별하는 expression을 먼저 보지만 do-while 문은 loop이 먼저 실행되고 expression을 판별한다. 즉, do-while 문은 최소 한 번 이상 loop가 실행된다.int count = 0; do { System.out.println(count); count++; } while(count < 10);(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
for statement
대부분의 반복 구문은 counter나 state를 기록하는 변수가 존재하고 loop 과정동안 참/거짓이 판별된다. for 문은 이러한 변수의 initialize, update 과정을 더욱 명백하게 만들어주는 문법 구조를 가지고 있다.
// while 문의 initialize, update 과정이 다음과 같다면,
initialize;
while (test) {
statement;
update;
}// for 문의 initialize, update 과정이 다음과 같다.
for (initialize; test; update) {
statement
}/*
위에서 while 문으로 구현한 반복문을 for 문 형식으로
동일한 기능을 구현한 예제이다.
*/
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++) {
System.out.println(count);// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
}/*
comma(,)를 사용하여 multiple initialization과 update도 가능하다.
*/
for (int i = 0, j = 10; i < 10; i++, j--) {
sum += i * j;
}/*
for 문은 계수(counting numbers)에만 국한되어 있지 않다.
예를 들어, 연결리스트(Linked List)에서 iterate도 가능하다.
*/
for (Node n = listHead; n != null; n = n.nextNode()) {
process(n);
}/*
for 문의 initialize, update, test 구문은 각각 생략 가능하다.
*/
for (;;) {
// 이렇게 실행하면 항상 참이 되어 무한 루프가 된다.
}(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
foreach statement
foreach 문은 Object를 다루는 데에 있어 불필요하게 투박한 부분들을 제거한 구문이다. 그러나 foreach 구문이라고 해서 each라는 키워드가 존재하지는 않는다. 위 반복문들에서 10개의 숫자를 출력한 것과 동일한 기능을 구현할 수 있다. 그러나 iterate할 수 있는 컬렉션이 필요하다는 것이 차이점이다.// These are the numbers we wnat to print int[] primes = new int[] {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29}; // This is the loop that prints them for (int n : primes) System.out.println(n);(소스코드 출처: O'Reilly, <Java in a Nutshell 7th edition>)
(출처: https://soshace.com/guide-to-control-flow-statements-in-java/)
'Languages > Java ☕️' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [java-live-study] 🌈 5주차 과제: 클래스 (0) | 2021.01.04 |
|---|---|
| You can not write Java code without defining a class. (0) | 2021.01.04 |
![[java-live-study] 🔥 4주차 과제: 제어문](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FqdsFf%2FbtqSAShjgGF%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAL2va9esoNdhgCdqJLIJG9j1uQI1NQXfhWl54cpjS9eU%2Fimg.jpg%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1761922799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3DfjfMepBhIIPPy2FTfieAKokiDYs%253D)